When it comes to understanding the human body, fibroblasts play a crucial role in maintaining skin health and overall tissue repair. These specialized cells are essential components of connective tissues, and their functions have far-reaching implications for wound healing, aging, and various medical conditions. In this article, we will delve deep into the world of fibroblasts, exploring their structure, functions, and significance in biological processes.
Have you ever wondered what makes your skin so resilient and capable of healing itself after an injury? The answer lies in the fascinating workings of fibroblasts. These remarkable cells are responsible for producing collagen, elastin, and other vital components that give skin its strength and flexibility. Understanding what fibroblasts are and how they function can help us appreciate the intricate mechanisms that keep our bodies healthy.
This article aims to provide a detailed overview of fibroblasts, their role in the body, and their importance in medical research. Whether you're a student, healthcare professional, or simply someone curious about the science behind skin health, this guide will offer valuable insights into the world of fibroblasts. Let's begin by exploring the basics of these incredible cells.
Read also:Iot Device Management With Aws Iot And Ssh A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents:
- What are Fibroblasts?
- Structure of Fibroblasts
- Functions of Fibroblasts
- Fibroblasts in Wound Healing
- Fibroblasts and Aging
- Fibroblasts in Disease
- Fibroblasts in Medical Research
- Fibroblasts and the Cosmetic Industry
- Measuring Fibroblast Activity
- Conclusion
What are Fibroblasts?
Fibroblasts are specialized cells found in connective tissues throughout the body. They are the primary producers of extracellular matrix components, such as collagen, elastin, and glycosaminoglycans, which provide structural support and elasticity to tissues. These cells are essential for maintaining the integrity of the skin, muscles, bones, and other organs. Understanding what fibroblasts are is key to grasping their importance in biological processes.
Types of Fibroblasts
There are several types of fibroblasts, each with specific roles depending on their location in the body:
- Dermal Fibroblasts: Found in the skin, these cells produce collagen and elastin, contributing to skin strength and flexibility.
- Periosteal Fibroblasts: Located in the bone, these cells help in bone repair and regeneration.
- Pleural Fibroblasts: Found in the lining of the lungs, these cells aid in maintaining lung elasticity.
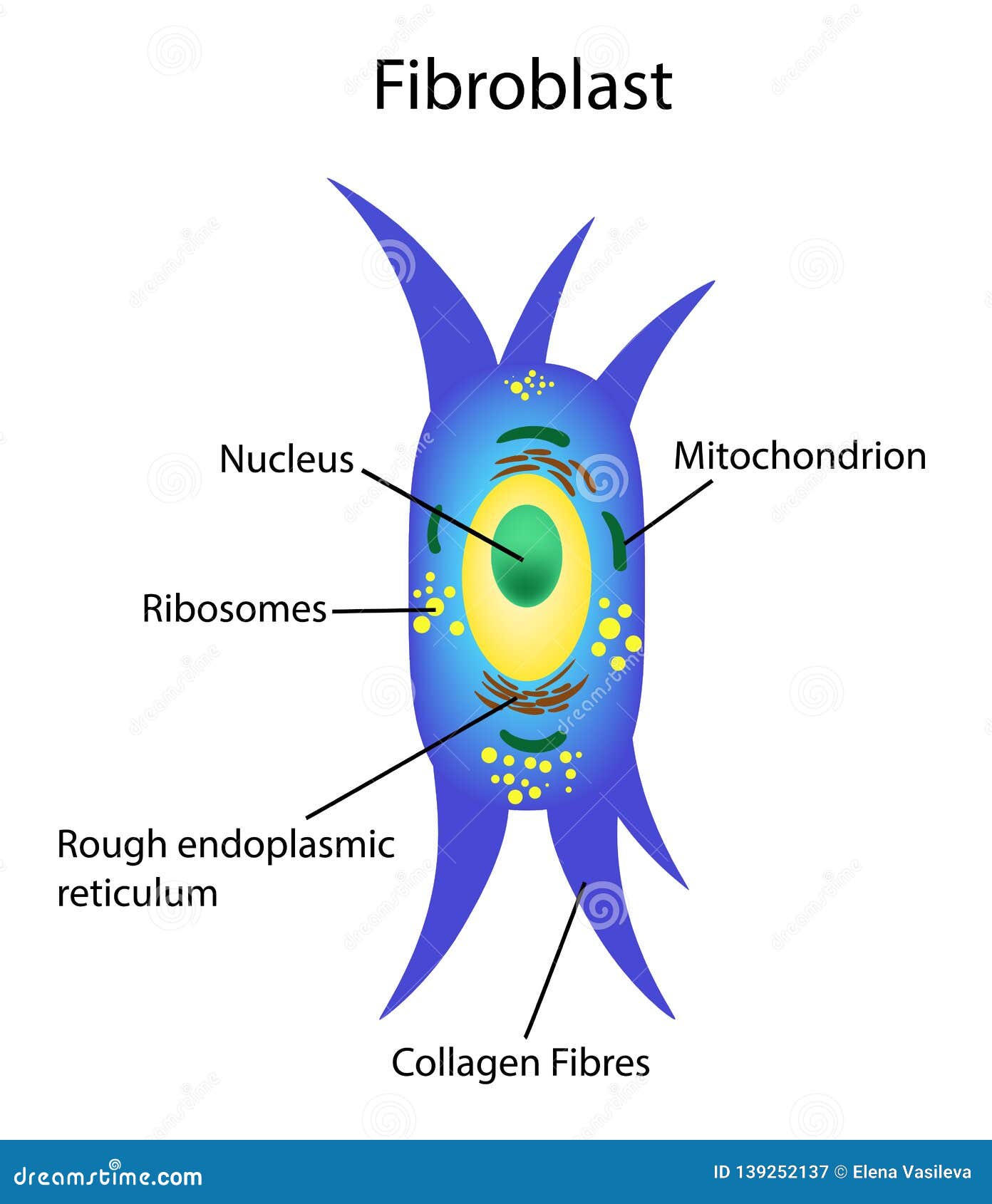
Structure of Fibroblasts
The structure of fibroblasts is designed to support their primary function of producing extracellular matrix components. These cells are typically elongated and spindle-shaped, with a large nucleus and abundant rough endoplasmic reticulum. This structure allows them to efficiently synthesize and secrete proteins such as collagen and elastin.
Key structural components of fibroblasts include:
- Nucleus: Contains genetic material and controls cellular activities.
- Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum: Responsible for protein synthesis.
- Golgi Apparatus: Modifies, packages, and secretes proteins for extracellular matrix production.
Functions of Fibroblasts
The primary functions of fibroblasts revolve around the production and maintenance of the extracellular matrix. These cells are responsible for:
Read also:Who Is Lauren Bricken Discovering The Remarkable Journey Of Lauren Bricken
- Collagen Production: Collagen is the main structural protein in the body, providing strength and support to tissues.
- Elastin Synthesis: Elastin gives tissues the ability to stretch and return to their original shape.
- Wound Healing: Fibroblasts play a critical role in repairing damaged tissues by producing new extracellular matrix components.
How Fibroblasts Support Tissue Repair
Fibroblasts are activated during the inflammatory phase of wound healing. They migrate to the injury site, proliferate, and produce collagen and other matrix proteins to close the wound and restore tissue integrity.
Fibroblasts in Wound Healing
Wound healing is a complex process involving multiple cell types, and fibroblasts are central to this process. They are responsible for producing the extracellular matrix that forms the foundation of new tissue. Without fibroblasts, wounds would not heal properly, leading to chronic conditions such as ulcers or scars.
According to a study published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, fibroblasts secrete growth factors that stimulate cell proliferation and migration during wound healing. This highlights their importance in the recovery process.
Fibroblasts and Aging
As we age, the activity of fibroblasts decreases, leading to a reduction in collagen and elastin production. This decline contributes to the visible signs of aging, such as wrinkles and loss of skin elasticity. Understanding how fibroblasts function in aging can help develop anti-aging treatments.
Factors Affecting Fibroblast Activity
Several factors influence fibroblast activity, including:
- Genetic Factors: Some individuals have naturally more active fibroblasts, leading to better skin health.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to UV radiation and pollutants can damage fibroblasts, reducing their ability to produce collagen.
- Lifestyle Choices: A healthy diet and regular exercise can support fibroblast function and promote skin health.
Fibroblasts in Disease
Fibroblasts are involved in various diseases, including fibrosis, cancer, and autoimmune conditions. In fibrosis, fibroblasts produce excessive extracellular matrix components, leading to tissue scarring. In cancer, fibroblasts can promote tumor growth by creating a supportive microenvironment.
A study published in Nature Reviews Cancer highlights the role of fibroblasts in cancer progression, emphasizing the need for targeted therapies that modulate fibroblast activity.
Fibroblasts in Medical Research
Medical research on fibroblasts has led to significant advancements in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering. Scientists are exploring ways to harness the power of fibroblasts to repair damaged tissues and organs. For example, fibroblast-based therapies are being developed to treat burns, ulcers, and other conditions involving tissue loss.
Emerging Technologies
Some of the emerging technologies in fibroblast research include:
- Gene Therapy: Modifying fibroblasts to enhance their regenerative capabilities.
- Stem Cell Research: Using stem cells to generate functional fibroblasts for tissue repair.
- 3D Printing: Creating bioengineered tissues using fibroblasts as building blocks.
Fibroblasts and the Cosmetic Industry
The cosmetic industry has embraced the potential of fibroblasts to improve skin health and combat aging. Anti-aging creams, serums, and treatments often target fibroblast activity to boost collagen production and enhance skin elasticity.
Popular Treatments
Some popular treatments that stimulate fibroblasts include:
- Microneedling: A procedure that uses tiny needles to create micro-injuries, activating fibroblasts and promoting collagen production.
- Laser Therapy: Uses light energy to stimulate fibroblasts and improve skin texture.
- Dermal Fillers: Injectables that mimic the effects of fibroblasts by providing immediate volume and support.
Measuring Fibroblast Activity
Scientists use various methods to measure fibroblast activity, including:
- Collagen Assays: Quantifying collagen production as an indicator of fibroblast function.
- Gene Expression Analysis: Measuring the expression of genes involved in fibroblast activity.
- Cell Culture Studies: Observing fibroblast behavior in controlled laboratory settings.
Conclusion
Fibroblasts are essential cells that play a vital role in maintaining tissue health and supporting the body's natural repair processes. From wound healing to aging and disease, their functions are far-reaching and impactful. By understanding what fibroblasts are and how they work, we can develop better treatments and therapies to improve human health.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments section below. If you found this article helpful, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from the information. For more insights into health and science, explore our other articles on the website.